Description
Stem cells offer a therapeutic promise for many diseases. In the case of diabetes, stem cells offer the promise that beta cells may be generated ex vivo for the possible transplantation and cure of Type I diabetes (Couri CE, et al. ). For this to happen, stem cells will need to be isolated and expanded, they will need to be differentiated toward the beta cell lineage, and the differentiated cell progeny used for transplantation may need to be isolated from complex cell mixtures following differentiation. Appropriate markers targeting cell surface molecules on developing and mature pancreatic cells will be required for such research.
Specifications
| Antigen | HPSE |
| Classification | Polyclonal |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Gene | HPSE |
| Gene Alias | Endo-glucoronidase; endoglycosidase heparanase; HEP; Heparanase; Heparanase 50 kDa subunit; Heparanase 8 kDa subunit; Heparanase-1; heparanase-like; Hpa; HPA1; HPR1; HPSE; HPSE1; HSE1 |
| Host Species | Rabbit |
| Purification Method | Protein G |
| Regulatory Status | RUO |
| Gene ID (Entrez) | 10855 |
| Content And Storage | -20°C or -80°C if preferred |
| Form | Liquid |
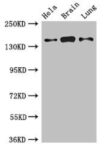
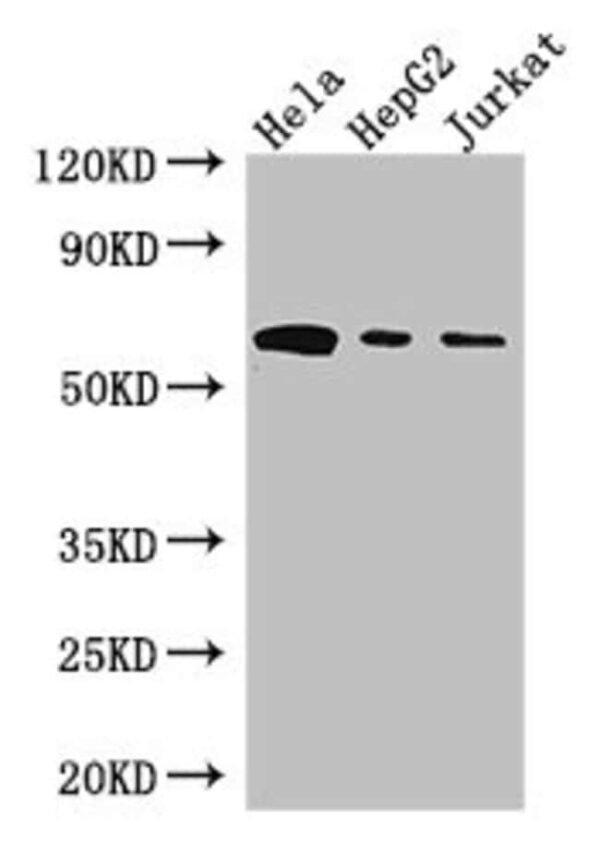
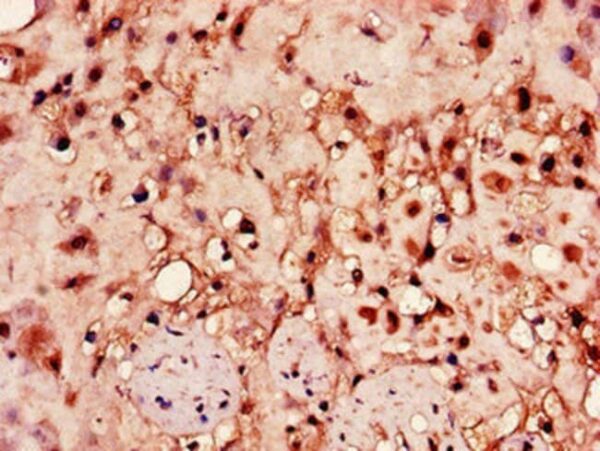
| Applications | ELISA, Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin), Western Blot |
| Concentration | 3 mg/mL |
| Formulation | PBS with 50% glycerol and 0.03% ProClin 300; pH 7.4 |
| Gene Accession No. | Q9Y251 |
| Gene Symbols | HPSE |
| Immunogen | Recombinant Human Heparanase protein (263-523AA) |
| Quantity | 100 μg |
| Primary or Secondary | Primary |
| Target Species | Human |
| Product Type | Antibody |
| Isotype | IgG |





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.